Medication Administration Record Sheet PDF Form
The Medication Administration Record Sheet is a vital document used to track the administration of medications to individuals. This form ensures that all medication doses are recorded accurately, promoting safety and accountability in medication management. To get started with filling out the form, click the button below.
Launch Editor
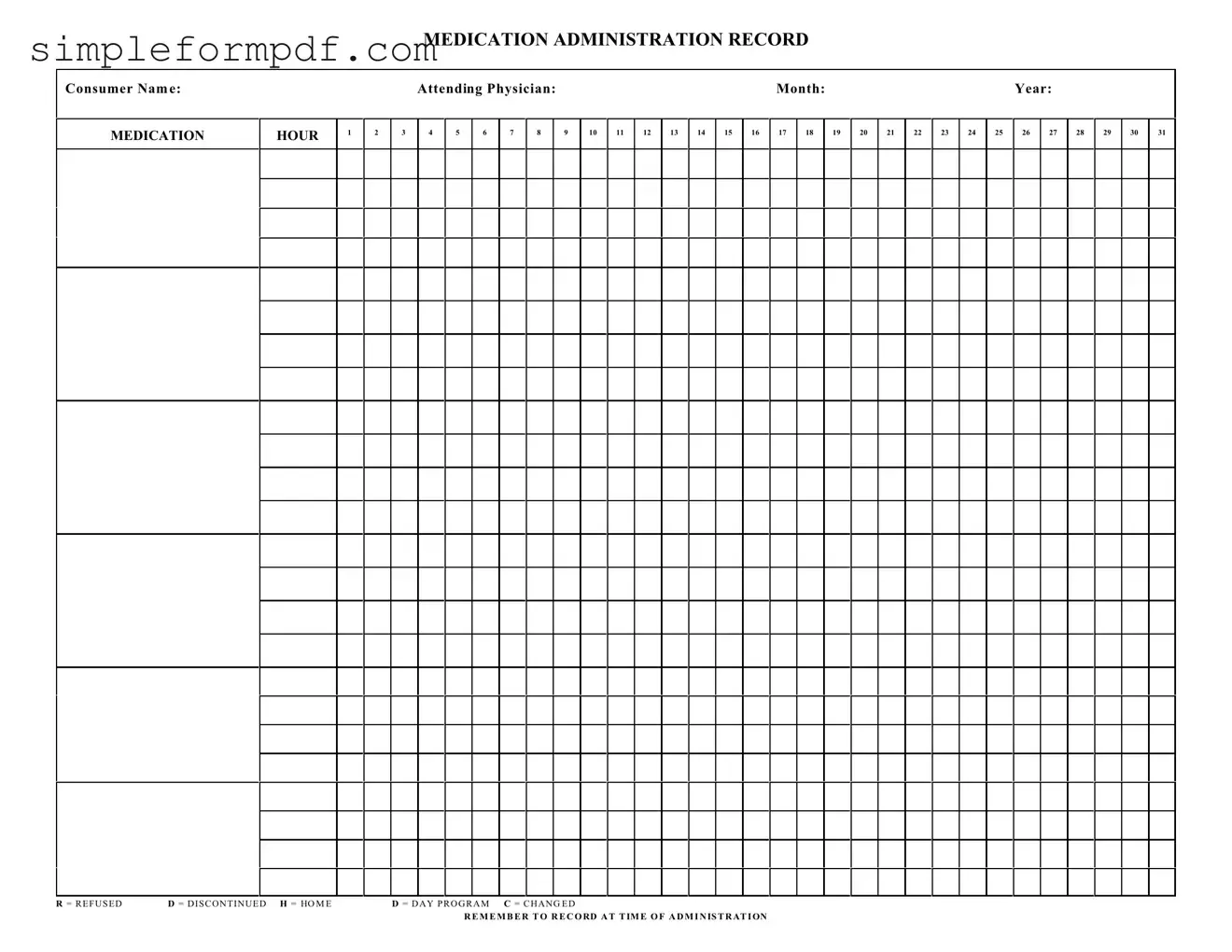
Medication Administration Record Sheet PDF Form
Launch Editor
Need instant form completion?
Finish Medication Administration Record Sheet online in just a few minutes.
Launch Editor
or
Download PDF